Product docs and API reference are now on Akamai TechDocs.
Search product docs.
Search for “” in product docs.
Search API reference.
Search for “” in API reference.
Search Results
results matching
results
No Results
Filters
Backing up Gitlab on Linode Object Storage
In This Guide
GitLab is a complete solution for all aspects of your software development. At its core, GitLab serves as your centralized remote Git repository. GitLab also features built-in tools that represent every task in your development workflow, from planning to testing to releasing.
All modern GitLab installations additionally include tooling to create backups on Linode’s Object Storage using a single command. This guide will describe the process for initially setting up an Object Storage Bucket which can be used to remotely store backups created directly from Gitlab.
Before you Begin
Follow the guide for Deploying Gitlab Through the Linode Marketplace to completion, or otherwise ensure that a Gitlab installation is available and accessible over SSH.
Create an Object Storage access key and a bucket. See the Manage Access Keys and Create and Manage Buckets](/docs/products/storage/object-storage/guides/manage-buckets/) guides.
Configuring Gitlab For Object Storage Backups
In order to configure Gitlab on Linode’s Object Storage, the Gitlab instance must first be Accessed Directly Over SSH. To do this, enter the following command, replacing the username and IP address with the unique username and IP address of your Linode:
ssh username@198.51.100.4
Once access has been gained, using a text editor of your choice, edit the ‘/etc/gitlab/gitlab.rb’ configuration file to reflect the following:
sudo nano /etc/gitlab/gitlab.rb
- File: /etc/gitlab/gitlab.rb
gitlab_rails['backup_upload_connection'] = { 'provider' => 'AWS', 'region' => 'us-east-1', 'endpoint' => 'https://us-east-1.linodeobjects.com', 'aws_access_key_id' =>YOUR_ACCESS_KEY, 'aws_secret_access_key' =>YOUR_SECRET_KEY, } gitlab_rails['backup_upload_remote_directory'] = 'bucketname'
The following chart will explain each configuration settings in additional detail:
| Descriptor | Setting |
|---|---|
provider | AWS (The provider must be set to AWS because it is dependent on s3cmd) |
region | The region the bucket was created in. A full list of regions can be found in the Product Documentation. |
endpoint | The endpoint url for the data center. Uses the syntax of region.linodeobjects.com |
aws_access_key-id | The Object Storage Access Key created in a previous step. |
aws_secret_access_key | The Object Storage Secret Key created in a previous step. |
gitlab_rails['backup_upload_remote_directory'] | The label of the bucket created during bucket creation. |
Once the configuration settings are completed, apply the configuration with the following command:
gitlab-ctl reconfigure
Creating a Backup
Once configured, backups can now be created for your gitlab instance at any time by using the following command:
gitlab-backup create
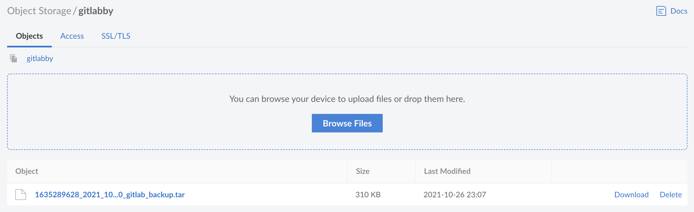
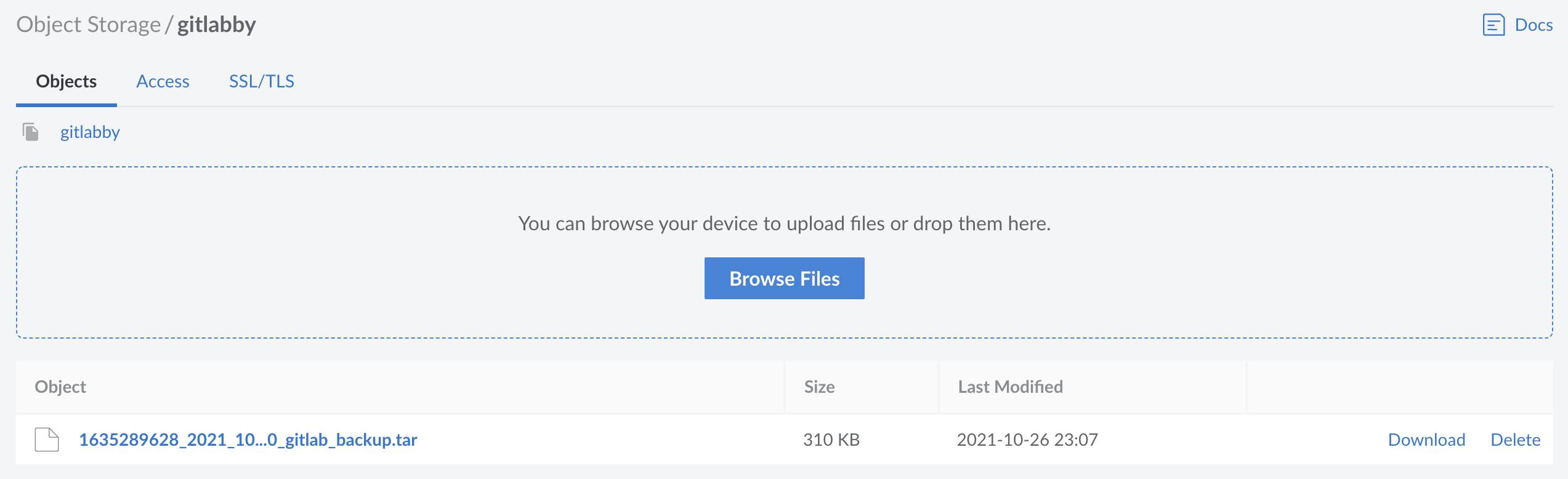
Once complete, the backup will be freely available in a compressed .tar file within the Object Storage bucket, and can be observed directly in the Linode Cloud Manager.


This page was originally published on