Product docs and API reference are now on Akamai TechDocs.
Search product docs.
Search for “” in product docs.
Search API reference.
Search for “” in API reference.
Search Results
results matching
results
No Results
Filters
Debian Security
This bundle of guides shows how to securely connect to a Debian compute instance and how to harden it from attacks using public SSH keys, firewalls, AV software, and other tools.
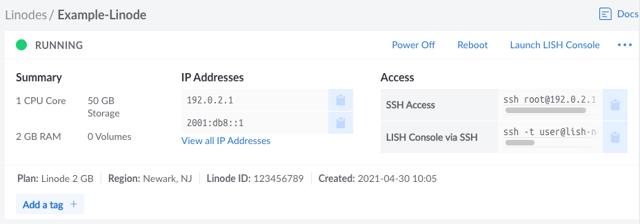
Setting Up and Securing a Compute Instance
After you have successfully created a Compute Instance, there are a few initial configuration steps you should perform within your new Linux system. This includes updating your system, setting the timezone, configuring a custom hostname, adding a limited user, hardening SSH to prevent unauthorized access, and configuring a firewall. These steps ensure your instance is up to date, secure, and ready for use.
Get Started with nftables
nftables replaces the successful iptables and its related frameworks built on Netfilter. With nftables come improvements to performance and usability, but also significant changes to syntax and usage. Use this guide to get started learning about what nftables is and how it differs from iptables. Follow along with this guide’s example to implement your own rules in nftables and get a hands-on idea of what it can do.

Securing MySQL Server
MySQL
MySQL is an open-source relational database management system. This guide will show you how to secure and audit a MySQL server. The name is a combination of “My”, the name of co-founder Michael Widenius’s daughter, and “SQL”, the abbreviation for Structured Query Language.
Cloud Firewall
Linode’s Cloud Firewall service is a robust cloud-based firewall solution available at no additional charge for Linode customers. Through this service, you can create, configure, and add stateful network-based firewalls to Linode Compute Instances and NodeBalancers.

Anti-Virus and Rootkit Protection with ClamAV and rkhunter
Anti-virus and Rootkit Detection
This guide teaches you how to use ClamAV, ClamTK, and rkhunter for anti-virus and rootkit detection to secure your server.

Install SELinux on Debian 10
Ubuntu has a Mandatory Access Control (MAC) system similar to SELinux, named AppArmor. Both SELinux and AppArmor provide a set of tools to isolate applications from each other to protect the host system from being compromised. AppArmor offers Ubuntu users mandatory access control options, without the perceived difficulty or learning curve that SELinux may have. However, if you are switching to Debian 10, are already familiar with SELinux, and would like to use it to enforce security on your system, you can install it by following the steps in this guide.

How to Configure a Firewall with UFW
What is UFW?
UFW, or uncomplicated firewall, is a frontend for managing firewall rules in Arch Linux, Debian, or Ubuntu. UFW is used through the command line (although it has GUIs available), and aims to make firewall configuration easy (or, uncomplicated).

Using Fail2ban to Secure Your Server
What is Fail2Ban
Fail2ban is a log-parsing application that monitors system logs for symptoms of an automated attack on your Linode. In this guide, you learn how to use Fail2ban to secure your server.
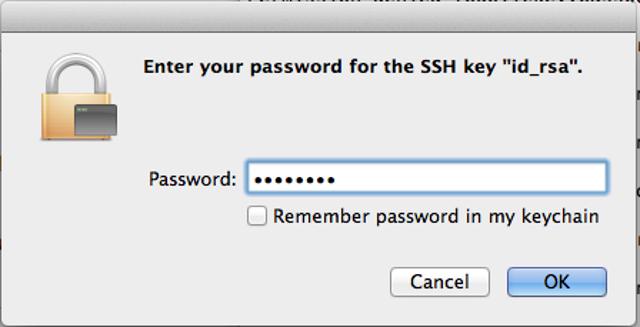
Use SSH Public Key Authentication on Linux, macOS, and Windows
Public key authentication with SSH (Secure Shell) is a method in which you generate and store on your computer a pair of cryptographic keys and then configure your server to recognize and accept your keys. Password authentication is the default method most SSH clients use to authenticate with remote servers, but it suffers from potential security vulnerabilities like brute-force login attempts. Using key-based authentication offers a range of benefits, including:
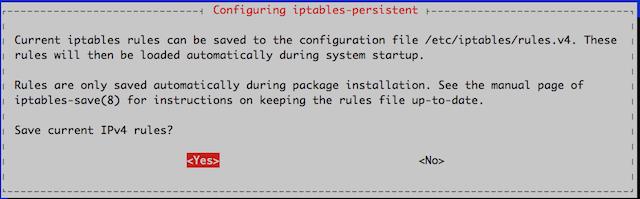
A Tutorial for Controlling Network Traffic with iptables
iptables is an application that allows users to configure specific rules that will be enforced by the kernel’s netfilter framework. It acts as a packet filter and firewall that examines and directs traffic based on port, protocol and other criteria. This guide will focus on the configuration and application of iptables rulesets and will provide examples of ways they are commonly used.

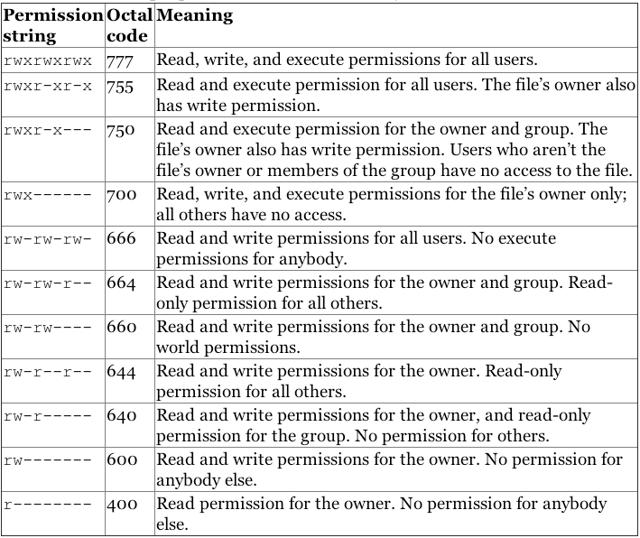
Modify File Permissions with chmod
Modify File Permissions with chmod
The chmod command allows users to change read and write permissions in Unix systems. This guide covers how to use chmod to view and modify these permission on files and directories.
Linux Users and Groups
If you are new to Linux/Unix, then the concept of permissions may be confusing. This guide provides you with an explanation of what permissions are, how they work, and how to manage them. A number of examples are provided to illustrate how to set and change permissions for both users and groups.

