This post is part of our Cloud Computing Foundations series. Build your skills further by taking our Introduction to Cloud Computing certification course.
Cloud computing is constantly changing, and staying on top of the latest practices and technologies is important to remain competitive. Whether you’re a seasoned cloud pro or just starting, our cloud certification course can give you valuable insights, enhance your skills, and equip you with the knowledge to optimize your cloud infrastructure.
In this Introduction to Cloud Computing series, we’ll explore the technology that makes cloud computing possible, different cloud service models, and the basics of essential application components like web servers and databases.
What is Cloud Computing?
Cloud computing is a model in which a third party enables you to deliver on-demand computing resources over the internet. Instead of managing hardware and software infrastructure, you can access computing resources like virtual machines and storage via a cloud provider.
Before cloud computing, organizations directly invested in expensive hardware and software and maintained their on-premise infrastructure or worked directly with data centers to colocate their infrastructure. As a result of costly upfront investments and limited scalability, demand increased for a solution that was more affordable, scalable, and easier to manage. Cloud computing offers a range of solutions that fit the bill—from simple, on-demand servers that are quick to provision to third-party-managed platforms that include enterprise-ready services.
Cloud computing is now leveraged by developers, growing businesses, and large corporations—for good reason.
Let’s dive into the benefits of cloud computing and why people use it in the first place.
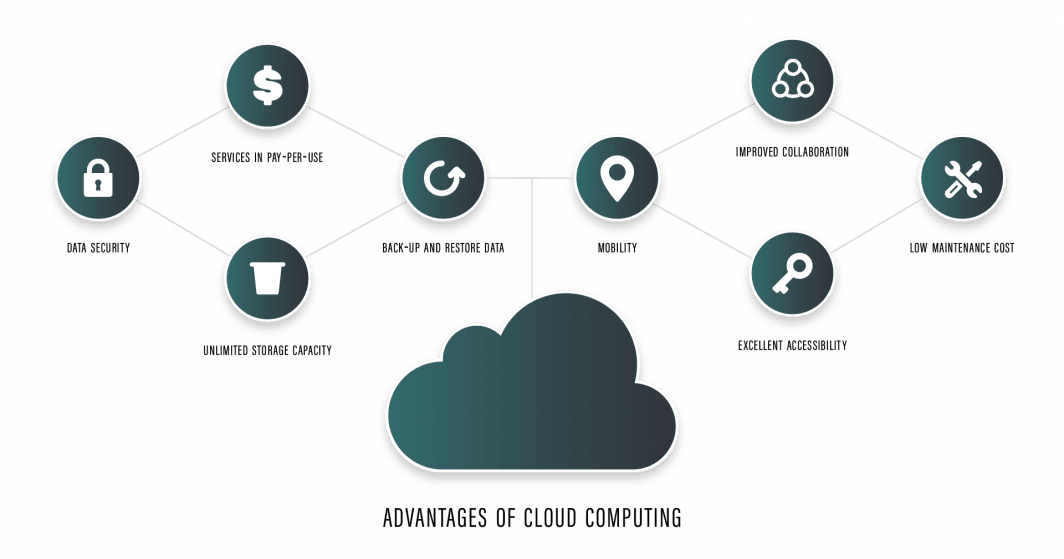
Benefits
According to McAfee’s Cloud and Risk Adoption Report, 87% of companies can accelerate and scale their businesses because of their use of cloud computing services. Whether you can serve more customers because you can easily scale in the cloud or provide more lucrative services because your cloud provider upgrades and maintains their software and hardware, the cloud helps businesses provide the best to customers.
Let’s take a closer look at the business benefits:
- Cost efficiency
- Agility
- Scalability
- Reliability
- Security
Cost Efficiency
With cloud computing, organizations can easily provision the exact resources they need when they need them. This means that businesses don’t need to invest in expensive hardware or software, and they can easily scale their resources up or down as needed.
Cloud service providers are responsible for maintaining and upgrading the data centers that house client applications and data, which saves organizations the ongoing expenses of purchasing, maintaining, and housing IT infrastructure.
Agility
You can deploy highly customized virtual instances in minutes, allowing them to focus on their business or customer needs rather than the infrastructure required to support them. This agility makes experimenting with new ideas and features easier while quickly testing them in a development environment to ensure stability and shipping to production.
Scalability
Scalability and elasticity enable you to allocate resources to meet fluctuating demand dynamically. The cloud offers a pay-as-you-go pricing model. You only pay for resources as you consume them. Adding or replacing resources like changing compute plan sizes or adding storage capacity is also easy allowing businesses to scale as they grow.
Reliability
Reliability, and business continuity, significantly benefit from cloud computing. If one aspect of the infrastructure fails, multiple operational links ensure that the network is working to the greatest extent possible.
Cloud service providers focus entirely on maintaining and improving their cloud infrastructure, resulting in data centers with the highest-performing compute, storage, and network resources.
Most cloud service providers offer fault tolerance and automatic data backups, so you can rest easy knowing that you can roll back in case of a bad code change or incident. This is especially important in today’s business environment, where data is critical to success and downtime can have a significant impact on the bottom line.
Security
Cloud providers focus their efforts on maintaining and improving their cloud infrastructure, resulting in data centers with the most secure network and infrastructure, which helps businesses keep their customer and application data safe. In fact, McAfee reports that 52% of companies experience improved security when using cloud services over traditional on-premises data centers.
However, there are multiple security layers, and your cloud provider is just one. It is also up to you to perform due diligence through both infrastructure and software to ensure their application is secure.
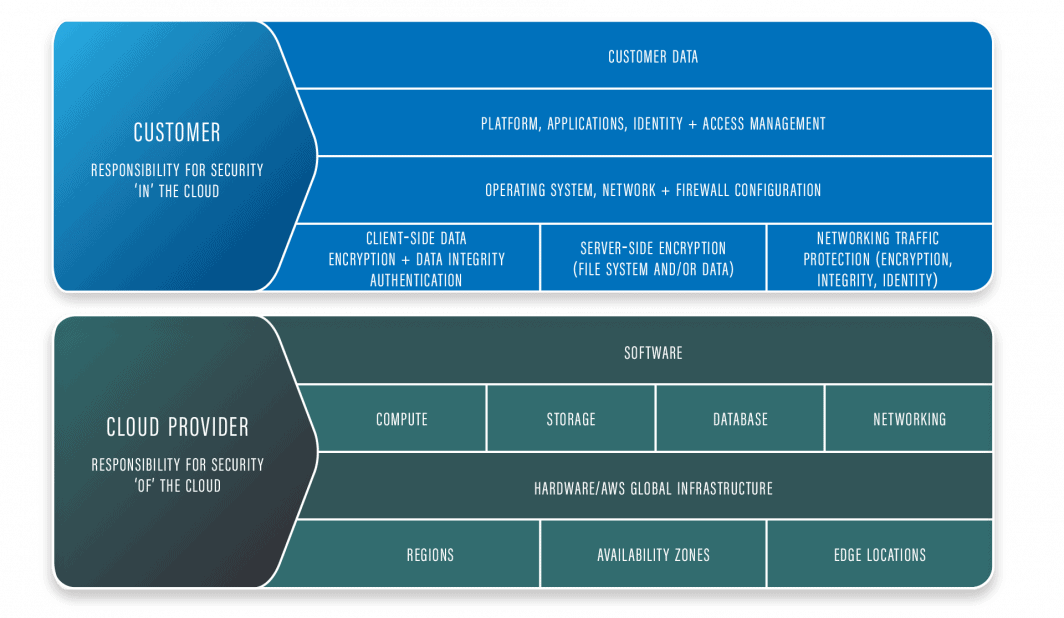
This is called a shared responsibility model.
A shared responsibility model relieves you of some security maintenance since the cloud provider is responsible for the security of the cloud hardware and software components of the infrastructure. This model requires you, however, to be responsible for the security in the cloud, including OS, apps, firewalls, and customer data.
Build the skills to succeed in cloud computing by taking our Introduction to Cloud Computing certification course.




Comments